In a broad sense, biomaterials would be materials designed to interact with biological systems in order to evaluate, treat, augment or replace any tissue, organ or function of the body.
Biomaterials are intended for the manufacture of components, parts or medical devices and systems for application in living beings, so they must be biocompatible. Those that have little or no influence on surrounding living tissue are called bioinert, while those that can bind to living bone tissue are called bioactive. Likewise, biomaterials can be of artificial origin (metals, ceramics, polymers) or biological (collagen, chitin, etc.).
Depending on the nature of the artificial material with which an implant is manufactured, a classification can be established in ceramic, metallic, polymeric or composite materials:
- Bioceramics are used in the manufacture of implants that do not have to support loads, as is the case in middle ear surgery, in the filling of bone defects in both oral and orthopedic surgery, and in the coating of dental implants and metal joints.
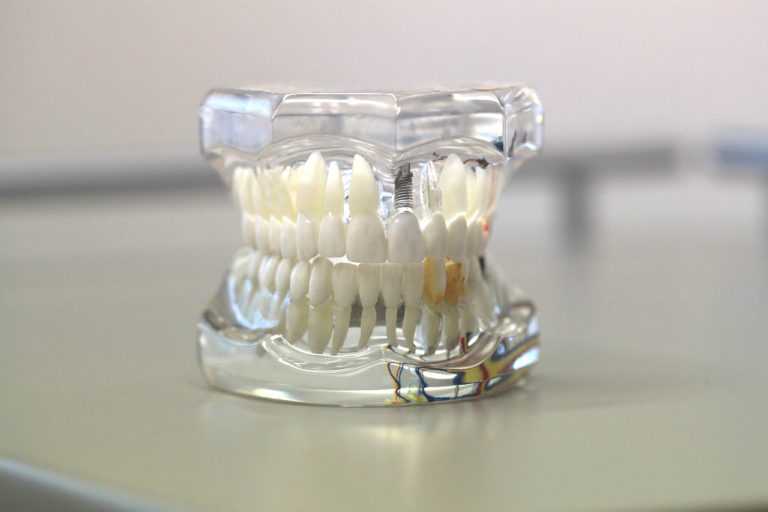
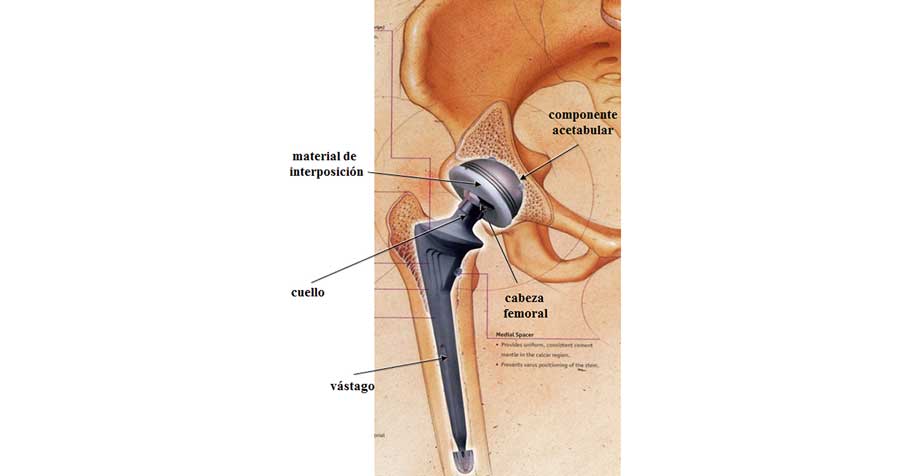
- Metallic ones are used when it is essential to support loads, as occurs in hip prostheses, for which alloys of cobalt (Co) with chromium (Cr) or titanium (Ti) with aluminum (Al) and vanadium (V) are used. titanium is also used in dental implants
- Polymeric biomaterials are widely used in clinics, both in surgical implants and in protective membranes, drug de delivery systems or acrylic bone cements.


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario